The Importance of Regular Diabetes Screening & Early Detection
By Dr. Saibal Chakravorty in Diabetes & Endocrinology
Nov 14, 2024
The Importance of Regular Diabetes Screenings & Early Detection
Diabetes is a long-term condition that disrupts the body’s ability to regulate blood glucose (sugar), a vital energy source. With the global rise in diabetes cases, regular screenings and early detection have become essential to managing and even preventing the severe health complications associated with the condition. Understanding the importance of diabetes screenings and early diagnosis can significantly improve quality of life, reduce healthcare costs, and help prevent the serious complications often linked to uncontrolled diabetes.
Why Regular Screenings Matter
Diabetes, particularly Type 2 diabetes, can develop slowly over time, often without noticeable symptoms. Many people with high blood sugar levels may not experience obvious signs until the disease has progressed, making regular screenings an invaluable tool. Regular screenings can detect prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are elevated but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Prediabetes is a warning signal and an opportunity for early intervention that can prevent the development of full-blown diabetes through lifestyle changes like a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management.
Diabetes screenings are especially important for individuals at higher risk. Risk factors include being overweight, having a family history of diabetes, being over the age of 45, leading a sedentary lifestyle, or having certain ethnic backgrounds with a higher prevalence of diabetes. Additionally, conditions like high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels, or a history of gestational diabetes can increase the likelihood of developing Type 2 diabetes. Screenings help people with these risk factors catch the disease in its early stages, before complications set in.
Benefits of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetes or prediabetes through regular screenings allows individuals to start managing the condition early, greatly reducing the risk of complications. Diabetes is associated with a range of serious health issues, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. When diabetes is diagnosed early, treatment can begin sooner, allowing individuals to control blood sugar levels effectively. Early management may involve lifestyle modifications, medication, or a combination of both, which can prevent the escalation of the disease and lower the risk of long-term complications.
Early diagnosis also has psychological benefits. It allows individuals to understand the condition and actively manage it, giving them a sense of control over their health. They can work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan that addresses their unique needs, empowering them to make informed choices about their health and lifestyle.
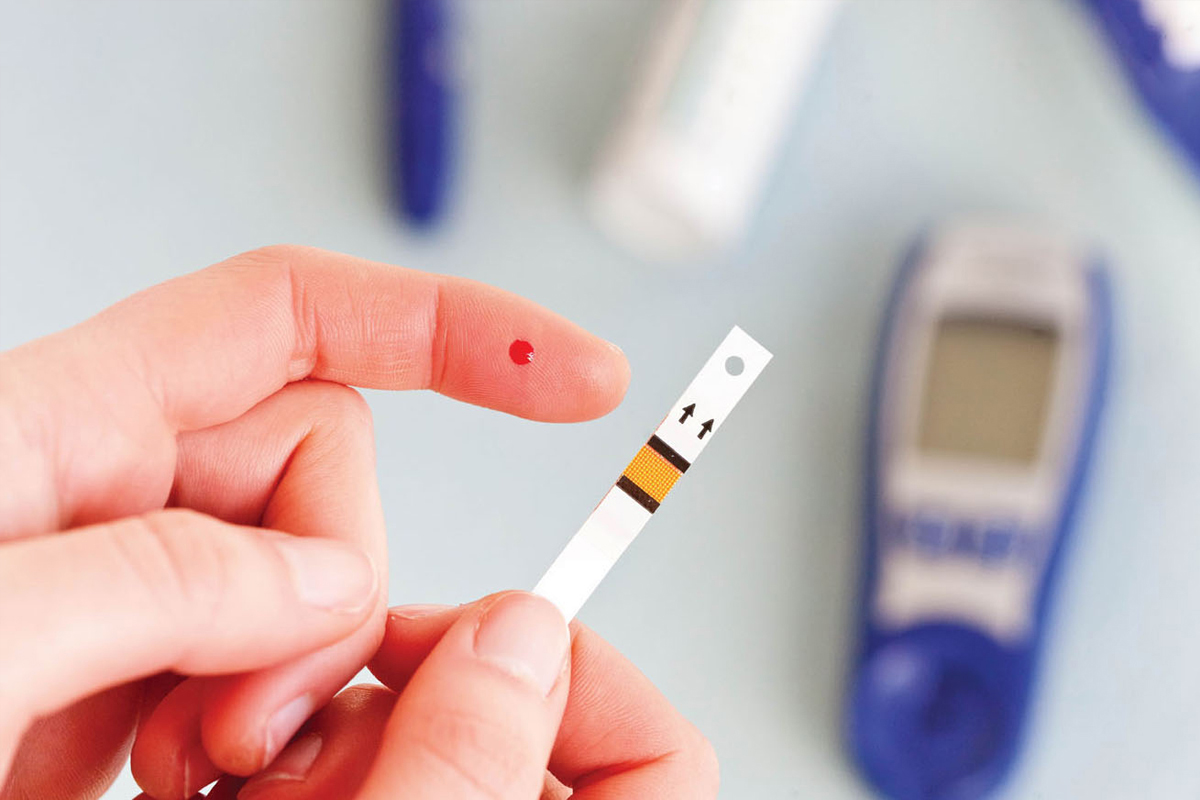
Types of Diabetes Screenings
Several tests are commonly used for diabetes screening. The most widely used tests include:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG): This test measures blood sugar levels following an overnight fast. Levels above 126 mg/dL indicate diabetes.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): After fasting, the individual drinks a sugary solution, and blood sugar levels are tested after two hours. A reading above 200 mg/dL may indicate a diagnosis of diabetes.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test: This blood test shows the average blood sugar levels over the past three months. An A1c level of 6.5% or greater suggests the diagnosis of diabetes.
- Random Plasma Glucose Test: This test measures blood sugar at any time of day, without fasting. A level above 200 mg/dL may indicate diabetes in individuals showing symptoms.
Each test has its advantages, and healthcare providers often recommend a specific test based on individual risk factors and health history. Regular screenings, especially for those at high risk, can make an enormous difference in detecting diabetes early.
Reducing Long-term Health Costs
Diabetes is a costly disease to manage, both for individuals and for healthcare systems. Complications arising from poorly controlled diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and amputation, can require extensive and expensive treatment. Regular screenings can help avoid these high costs by enabling early intervention and better long-term management of the disease. By detecting diabetes early and managing it effectively, individuals can reduce their need for costly medications, hospitalizations, and invasive procedures.
Embracing Preventive Care
Regular screenings embody a proactive approach to health. They enable individuals to understand and manage their risk, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and make informed decisions that can prevent diabetes or control it effectively if it does develop. Embracing preventive care by scheduling regular diabetes screenings and staying informed about the risks is an empowering way to protect one’s health and reduce the impact of this growing epidemic.