Choosing Between Angioplasty and Bypass Surgery: A Patient’s Guide
By Dr. Sameer Sharma in Cardiology Cardiac Surgery
Jan 13, 2025
When it comes to treating blocked coronary arteries, patients often face a crucial decision between angioplasty and bypass surgery. Both procedures aim to restore blood flow to the heart, but they differ in approach, recovery time, risks, and long-term outcomes. Understanding these differences can help patients make informed decisions in consultation with their doctors.
Also Read: Open Heart Surgery vs. Minimally Invasive Heart Surgery: Choosing the Right Approach
Understanding the Procedures
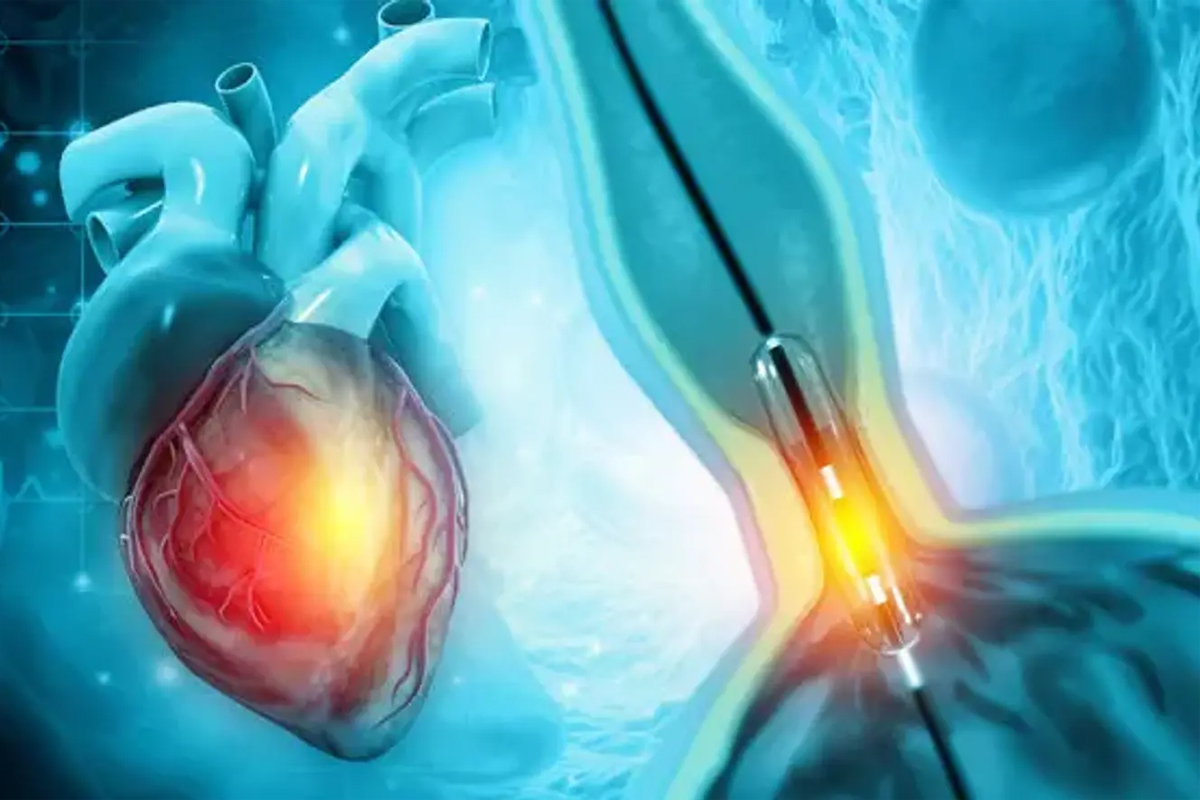
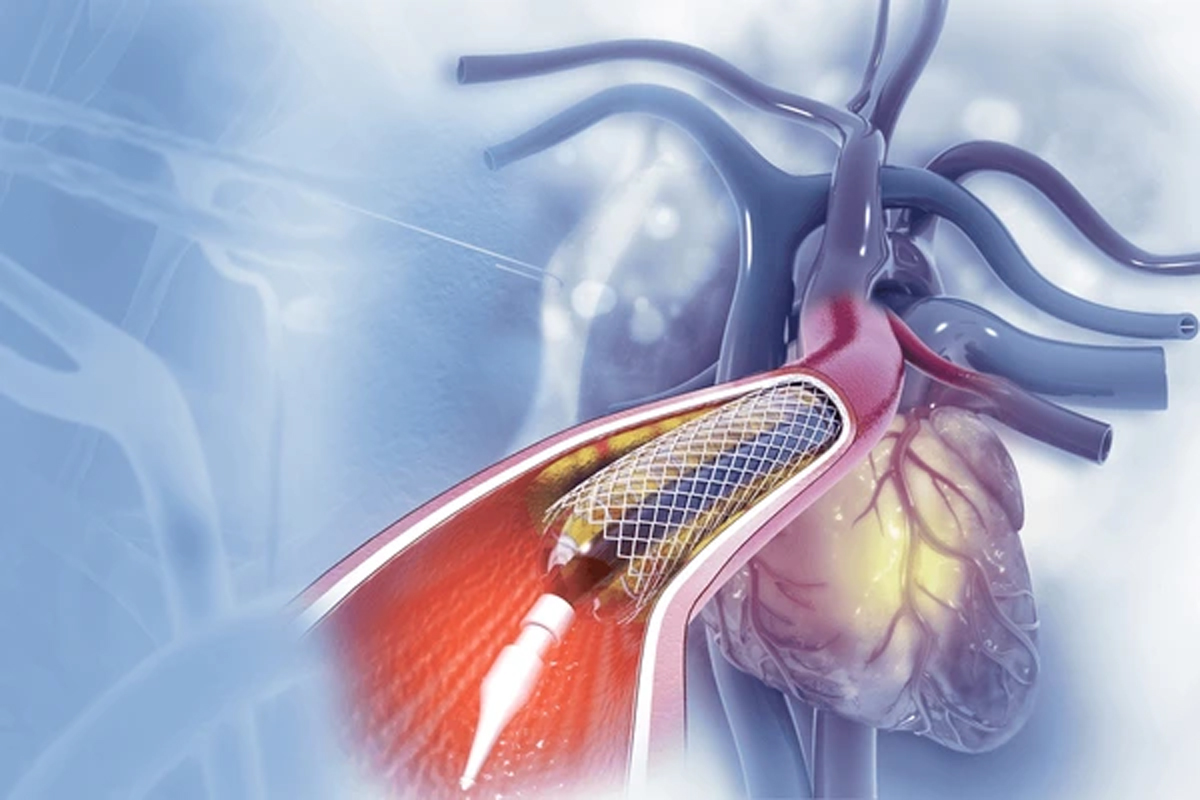
Angioplasty (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention – PCI)
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at opening narrowed or blocked arteries.A thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the blood vessel, usually in the groin or wrist, and guided to the blocked area. A tiny balloon at the catheter’s tip is inflated to compress plaque against the artery walls, restoring normal blood flow.A stent, a tiny wire mesh tube, is commonly placed to maintain the artery’s openness.
Also Read: What Age is Ideal for Heart Surgery? Factors and Considerations
Bypass Surgery (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting – CABG)
Bypass surgery is an open-heart procedure that involves creating a new pathway for blood to bypass the blocked arteries. This is done by grafting a healthy blood vessel, often taken from the leg, arm, or chest, onto the heart. The new blood vessel allows blood to flow around the blockage.
Key Factors to Consider
1. Severity of the Blockage
- Angioplasty: Best suited for patients with fewer blockages or less complex cases. It is typically advised when one or two arteries are impacted.
- Bypass Surgery: Preferred for patients with multiple blockages, severe narrowing in major arteries, or conditions like diabetes that make angioplasty less effective.
2. Recovery Time
- Angioplasty: Has a shorter recovery time. Most patients can return home within a day or two 7 resume normal activities within a week.
- Bypass Surgery: Requires a longer recovery period. Patients typically stay in the hospital for 4-7 days and need several weeks to regain full strength.
3. Risks and Complications
- Angioplasty: Risks include bleeding, artery re-narrowing (restenosis), and in rare cases, a heart attack or stroke during the procedure.
- Bypass Surgery: As a major surgery, it carries higher risks, including infections, blood clots, and complications related to anesthesia. However, it often provides longer-lasting results.
4. Long-Term Outcomes
- Angioplasty: Effective for many patients, but some may require repeat procedures if the arteries narrow again.
- Bypass Surgery: Offers more durable results, especially for patients with extensive blockages or conditions like diabetes.
5. Underlying Health Conditions
- Patients with diabetes, kidney disease, or severe heart disease may benefit more from bypass surgery due to its effectiveness in complex cases.
- For those with fewer health complications, angioplasty is often sufficient and less invasive.
Also Read: When Heart Surgery is Required and When It’s Not: Understanding the Necessities
Patient Preferences and Lifestyle Factors
Minimally Invasive vs. Invasive
- Angioplasty is less invasive, making it more appealing to patients who wish to avoid major surgery.
- Bypass surgery, while invasive, may be a better option for those seeking a more definitive and long-lasting solution.
Time for Recovery
- Patients with work or family obligations may prefer angioplasty for its quicker recovery time.
- Those who can accommodate a longer recovery period may opt for bypass surgery for its long-term benefits.
Cost Considerations
- Angioplasty is generally less expensive upfront but may require additional procedures in the future.
- Bypass surgery has a higher initial cost but may reduce the need for repeat interventions.
Consulting with Your Doctor
Choosing between angioplasty & bypass surgery is not a one-size-fits-all decision. Factors like the location and extent of blockages, overall health, and personal preferences all play a role. It’s essential to:
- Share your medical history & lifestyle details with your cardiologist.
- Ask about the potential benefits & risks of each procedure.
- Understand the long-term implications of your choice.
Conclusion
Both angioplasty and bypass surgery are effective treatments for blocked coronary arteries, but the right choice depends on individual circumstances. Angioplasty offers a less invasive solution with quicker recovery, while bypass surgery provides more comprehensive treatment for complex cases. By working closely with your doctor and understanding the pros and cons of each option, you can make a decision that best supports your heart health and overall well-being.
By
Director & Head Cardiovascular Surgeon
Metro MAS Hospital, Jaipur, Rajasthan