
Diabetes Education-File
By in Diabetes & Endocrinology
Nov 10, 2018
Q 1:- What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a medical condition where amount of glucose in the blood is higher than normal range because body cannot use it properly. This happens because either your pancreas can’t produce enough insulin or insulin does not work properly (known as insulin resistance).
Q 2:- What are types of diabetes?
(I) Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes develops if pancreas is unable to produce any insulin. type 1 diabetes usually develops in children and adolescents. Type 1 Diabetes is treated with daily insulin injections, a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
(ii) Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is most common diabetes, usually develops in adults (after 30 yrs of age). Type 2 Diabetes develops when pancreas can still make some insulin, but not enough or when the insulin that is produced does not work properly (knows as insulin resistance).Type 2 diabetes is treated with healthy diet and regular exercise. In addition to this, medications and/or insulin are often required.
(iii) Gestational Diabetes
Diabetes in pregnancy is called gestational diabetes. Women with gestational diabetes have increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in future.
(iv) Other types of diabetes
Diabetes seen in genetic syndromes, caused by defect in insulin secretion/action
Q 4:- Who is at risk developing Diabetes?
Anyone can develop diabetes but following factors increase risk of diabetes:
. If any of your close family member has diabetes (Parents, brother or sister)
. Overweight or obese (Body mass index >23) kg/m2
. No physical activity/ sedentary lifestyle
. Women who delivered a baby weighing > 4kg or were diagnosed with diabetes during pregnancy
. High blood pressure
. High blood cholesterol
. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
. Ischemic Heart disease patients
Q 5:- What are the symptoms of Diabetes?

Not all people with diabetes have symptoms, But few common symptoms of diabetes are:-
If you have any of these symptoms, you should get your blood glucose checked.
Q 6:- who should be investigated for diabetes?
After age of 40 years all people should get their blood glucose checked routinely even in absence of symptoms and risk factors. If your blood glucose is normal, you should get it checked regular once in 2-3 years.
Q 7:- How does diabetes affect one’s health?
Poorly managed diabetes can lead to various health complications over period of time. These complications include:
. Coronary heart disease, which can lead to a heart attack.
. Cerebrovascular disease, which can lead to stroke (Paralysis).
. Retinopathy (disease of the eye), which can lead to blindness.
. Nephropathy (disease of the kidney), which can lead to kidney failure and need for Dialysis.
. Neuropathy (disease of the nerves), which can lead to numbness, burning or loss of sensation in the feet ,ulceration of the foot requiring amputation.
. Erectile dysfunction etc.
Q 8:- How can I avoid these complications if I have diabetes?
Although diabetes cannot be cured, it can be successfully controlled. In order to stay away from complication, it is important that your blood glucose, blood pressure and blood cholesterol levels are adequately controlled. Eating a balanced diet, managing your weight and following a healthy lifestyle together with taking your prescribed treatment and regular monitoring is important.
Q 9:- Which are regular investigations required in diabetes?
- EVERY VISIT- Blood glucose, blood pressure
- 3 MONTHLY- HbA1c (Glycated hemoglobin)
This test gives estimate for average blood glucose control over past 3 months
- YEARLY- Kidney function test (KFT), lipid profile, fundus for diabetic retinopathy, urine for micro albumin, foot examination.
Q10:- What are the goals to achieve for good diabetes control?
- Pre meal blood glucose 70-130mg/dl
- Post meal blood glucose < 180mg/dl
- HbA1c (Glycated hemoglobin) < 7.0%
- Blood pressure < 140/90 mmHg
- LDL Cholesterol < 100 mg/dl
EXERCISE
Exercise with healthy eating is first step in management of diabetes mellitus. Benefits of regular exercise are:-

Improves blood glucose control
Decreases risk of heart disease

Decreases “bad”(LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides, increase “good”(HDL) Cholesterol

Helps in B.P control

Decreases Stress and improves quality of life
Go for at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity exercise daily like
- Brisk walking (outside or inside on a treadmill)
- Bicycling/Stationary cycling indoors
- Dancing
- Swimming or water aerobics
- Playing outdoor games
- Stair climbing
- Jogging/Running
- Moderate-to-heavy gardening
HYPOGLYCEMIA
In people with diabetes,blood glucose less than 70mg/dl is called hypoglycemia
Causes:-
. Missing or delaying meals Excess insulin/medication
. Unplanned or excessive exercise . Alcohol consumption
Treatment of hypoglycemia:-
CONSUME 15gm glucose (3teaspoon), Dissolved in 100ml water.
Recheck blood glucose after 15 minutes, If not better repeat the steps till blood glucose is > 100mg/dl
If the patient is Unconscious:-
. Do not give anything forcibly through mouth.
. Turn the patient to his left or right side.
. Rush to nearby hospital to give IV Glucose.
Prevention of hypoglycemia:-
. Do not skip meals
. Avoid prolonged or strenuous exercise than usual
. Limit alcohol intake and discuss with your doctor
. Adopt self monitoring of blood glucose
. Always carry glucose tablets or sugar sachet and identification card
. consult your doctor if blood glucose is lower than good control.
FOOT CARE
Keeping your blood sugar in good control and taking care of your feet every day can help you avoid serious foot problem like
. Infection . Ulceration
.Gangrene . Amputation of toe, foot or leg
Caring for your feet
Check your feet daily for cuts, blisters, scratches, red or black spots or swelling. If there is trouble in bending over to see the feet use a hand held mirror or ask a family member to help See your physician regularly and be sure that your feet are examined at each visit.
INSULIN
Blood glucose is regulated by insulin which is a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin acts like the key unlocking doors that allow glucose to enter cells. In diabetes, either the pancreas is unable to produce insulin or the cells do not respond to insulin’s effect.
WHO NEEDS INSULIN: The doctor will advise insulin administration:
. If you have Type 1 Diabetes
. If you are Type 2 and cannot meet blood glucose targets with oral diabetes medication.
. If you have significant complication such as ischemic heart disease, CVA, retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, hepatic (liver) complications, for whom oral diabetes medications are contraindicated.
. If you have an acute illness such as severe infection (Tuberculosis, urinary infection etc .or injury).
. If you are undergoing some surgical procedure.
. If you pregnant and have diabetes.
MYTHS & FACTS
Know your insulin better to fight diabetes better
Myth 1. Insulin is used in only late stage of diabetes.
Fact – Insulin can be used at any stage of diabetes. whenever blood sugars are very high i.e. > 300 mg/dl, insulin should be used to control diabetes rapidly. Insulin is advised to people with newly diagnosed diabetes as first treatment option if blood sugars are more than 300 mg/dl.
Myth 2. Once patient starts using insulin, he has to use it for lifetime.
Fact – Many times use of insulin is for short duration of time. use of insulin is not habit forming. insulin is used temporarily for many patients when they have infections, during surgery, during critical illness etc.
Myth 3. Insulin is harmful to kidneys and other organs.
Fact – Insulin in not harmful to any organ. in fact timely use of insulin can help people to control their diabetes and save them from ill effects of diabetes like heart attack, paralysis, kidney failure, diabetic retinopathy, foot problems etc.
Myth 4. Use of insulin is very complex procedure and it can NOT be managed at home.
Fact – With help of newer devices like insulin pens and ultra fine needles, self injection of insulin has become very easy with little training by medical personnel. Even children with type 1 diabetes are able to inject insulin themselves.
STORAGE: (8-250C)
. Protect your insulin (Bottles, pens, and cartridges) from extreme hot and cold temperature.
. If you are going outdoors for a while in hot or cold weather, store your insulin in an insulated case.
. Don’t store your insulin near radiators, heat vents, ovens, air conditioners etc.
. Never freeze (frozen insulin should be thrown away).
. Don’t leave your insulin in a closed car during very warm or cold weather.
. Never expose insulin to direct heat or light.
MODE OF INSULIN INJECTION
. Insulin Pen . Syringe
HOW TO INJECT INSULIN?
STEPS OF USING A PEN
123
4 5 6
7 8
- STEPS OF USING A SYRINGE
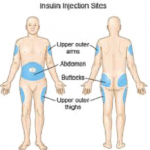
SITES OF INJECTION
DO’S and DONT’S to remember
- Do not use 100 IU syringe with 40 IU vial or vice versa.
- Do not injection insulin while bubbles are present in the syringe or the cartridge.
- Do not shake pen or vial of insulin, instead roll it gently.
- Rotate the sites of insulin injection.
- Hold the injection inside the skin for 10 seconds after pressing the dose dialer completely.
- Do not massage the injected area.
- The needle fixed on the insulin pen should be changed after maximum three pricks.
DIET FOR DIABETES IS A DIET FOR ALL

Department of Endocrinology
Endocrinology is division of medical science which deals with study of endocrine system of our body; Endocrine glands make various hormones which are essential for our health. Hormonal disorder can occur at any age from newborn to elderly. Common hormonal disorders are thyroid dysfunction, various types of diabetes mellitus, disorders of growth and sex development in children, sexual dysfunction, PCOS etc.
Book your appointment today if you have any of following problems….
- Diabetes mellitus (high blood glucose)
- Thyroid disorder
- Male infertility, erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, gynecomastia
- PCOS
- Hirsutism (male pattern hair growth in women)
- Late or early sexual development
- Child with poor height growth (growth hormone deficiency)
- Osteoporosis, disorders of calcium/phosphorus/sodium metabolism
- Obesity
- Disorders of adrenal and pituitary gland
Consult our Endocrinologist for appointment call on
(9560160808, 01294277777)







