Myths and Facts About Epilepsy: Debunking Common Misconceptions
By Dr. Puja Kushwah in Neurology
Nov 16, 2024
Myths and Facts About Epilepsy: Debunking Common Misconceptions
Epilepsy is one of the most misunderstood medical conditions, with many myths and misconceptions surrounding it. This neurological disorder affects millions of people worldwide, yet common misunderstandings persist. It’s crucial to separate fact from fiction to better support those living with epilepsy and raise awareness about the condition. Here, we’ll debunk some of the most widespread myths about epilepsy.
Myth 1: Epilepsy is a rare disorder.
Fact: Epilepsy is actually one of the most common neurological disorders in the world. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 50 million people globally have epilepsy, making it more common than many other health conditions. Epilepsy can impact individuals of all ages, races, and backgrounds.
Myth 2: Epilepsy only causes dramatic, full-body convulsions.
Fact: While many people associate epilepsy with grand mal seizures (which cause convulsions and unconsciousness), not all seizures look the same. There are various types of seizures, including focal seizures, which may cause brief periods of confusion, staring, or unusual sensations without a full-body convulsion. Some seizures may even go unnoticed by those around the individual.
Myth 3: People with Epilepsy Cannot Live Normal Lives
Fact: With proper treatment & management, most people with epilepsy can live normal, fulfilling lives. This includes going to school, working, and participating in activities like sports and driving (when seizures are well-controlled). Modern medication and treatments have greatly improved the quality of life for people with epilepsy.
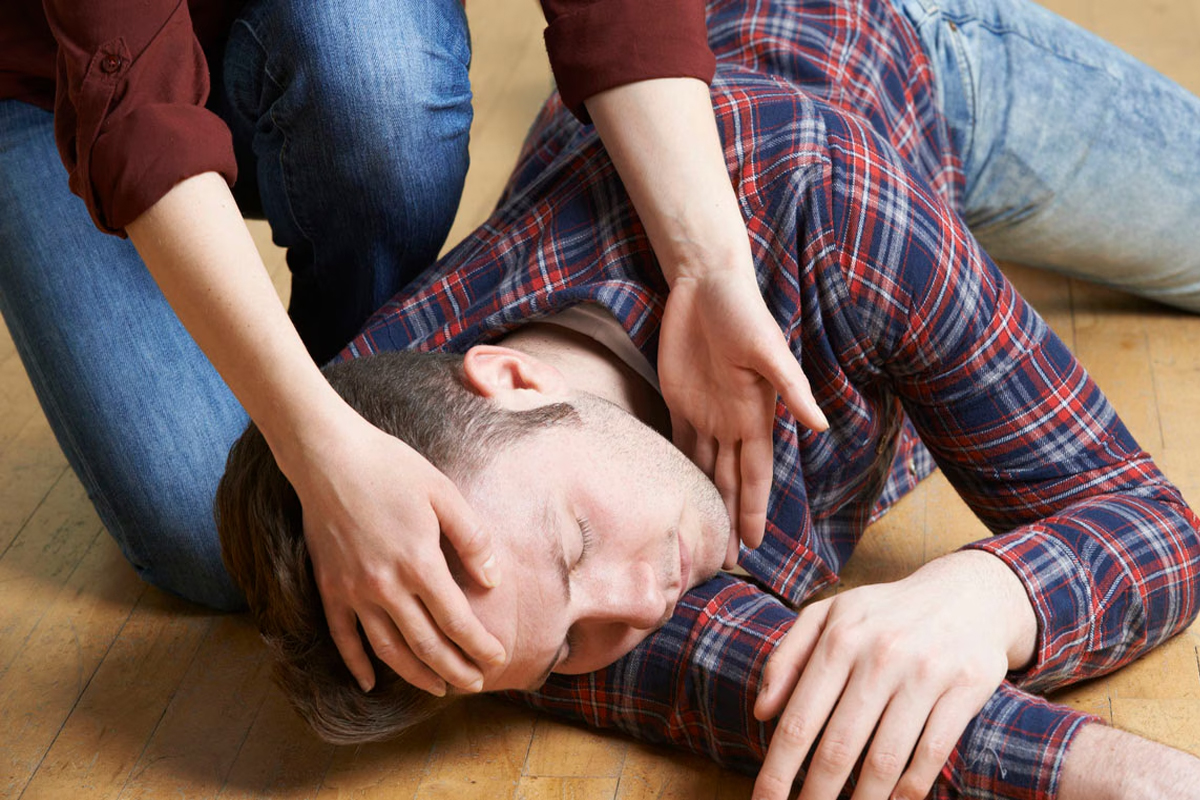
Myth 4: Seizures are always dangerous.
Fact: While seizures can be frightening to witness, they are not always life-threatening. Most seizures typically last only a few minutes and usually resolve on their own. However, if a seizure lasts longer than five minutes or if one seizure follows another without recovery, medical help should be sought immediately as this could indicate a more serious condition known as status epilepticus.
Myth 5: People with epilepsy can’t drive.
Fact: In many countries, people with epilepsy are allowed to drive once their seizures are well-controlled for a certain period (usually six to twelve months). The ability to drive depends on local laws and the individual’s seizure control, so it’s important to consult a doctor and follow the regulations.
Myth 6: Myth: It is possible to swallow your tongue during a seizure.
Fact: This is a common myth that has no basis in reality. During a seizure, it is not possible to swallow one’s tongue. However, individuals may bite their tongues, which can cause injury. It’s essential to avoid placing anything in the mouth of someone having a seizure, as this can lead to choking or further injury.
Myth 7: Epilepsy is caused by bad parenting or psychological trauma.
Fact: Epilepsy is not caused by bad parenting, stress, or trauma. While some forms of epilepsy can be genetic, others may result from brain injury, infection, or a variety of other medical conditions. It is important to understand that epilepsy is a medical condition that requires appropriate treatment.
Myth 8: Seizures are the result of possession or supernatural causes.
Fact: Throughout history, epilepsy was often misunderstood, and some cultures believed that seizures were caused by supernatural forces, such as possession by spirits or demons. Today, we know that epilepsy is a medical condition caused by abnormal brain activity, and it is not the result of any mystical forces.
Myth 9: People with epilepsy should avoid exercise or physical activity.
Fact: People with epilepsy can engage in regular physical activity, including exercise and sports. In fact, exercise is recommended as it helps improve overall health and may even reduce the frequency of seizures in some people. However, it is important for individuals with epilepsy to take safety precautions and avoid high-risk activities without proper supervision.
Myth 10: Epilepsy can’t be treated.
Fact: While there is no cure for epilepsy, it can usually be managed effectively with medication. In some cases, surgery, diet changes (such as the ketogenic diet), or other treatments may be considered. Many people with epilepsy experience fewer seizures or even become seizure-free with the right treatment plan.