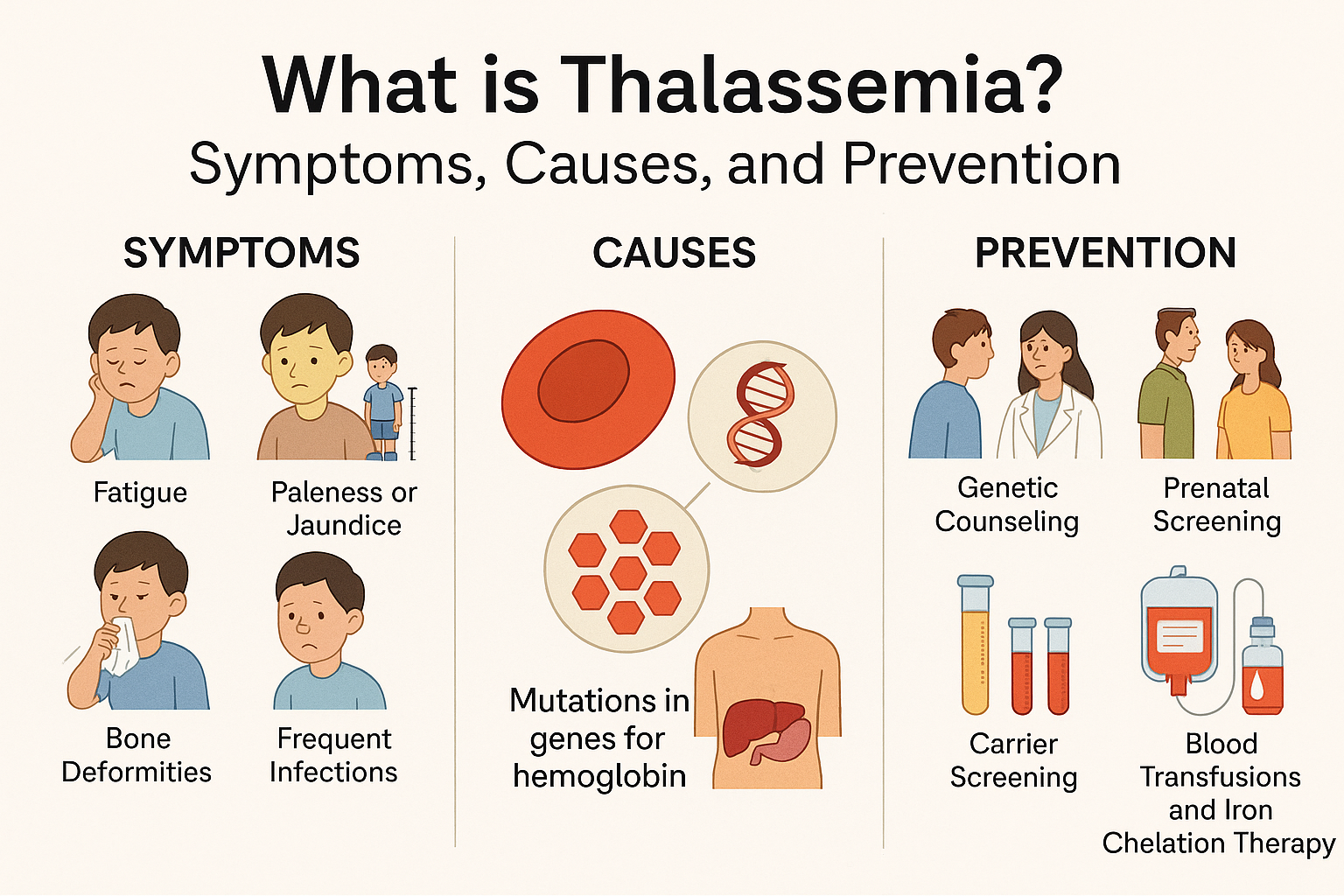
What is Cancer?
Cancer is a complex disease characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells within the body. These cells can invade nearby tissues and organs, disrupting their normal functions. If left unchecked, cancerous cells can metastasize, spreading to distant parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
How Does Cancer Happen?
Cancer develops when genetic mutations occur within normal cells, disrupting the mechanisms that regulate cell growth and division. These mutations can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, exposure to carcinogens such as tobacco smoke or UV radiation, unhealthy lifestyle choices, and certain infections.
Types of Cancer
Cancer manifests in numerous forms, each with its unique characteristics and treatment approaches. Some common types include:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Melanoma
- Pancreatic cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Bladder cancer
Recognizing Early Symptoms
Early detection plays a crucial role in improving cancer outcomes. While symptoms vary depending on the type and location of the cancer, some general warning signs include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, changes in bowel or bladder habits, unusual bleeding or discharge, and the presence of lumps or swelling.
Understanding Cancer Stages
Cancer staging helps classify the extent of the disease and guides treatment decisions. Staging typically involves evaluating the size and location of the primary tumor, lymph node involvement, and the presence of distant metastases. Stages range from 0 (in situ cancer) to IV (advanced cancer with widespread metastasis).
- Stage 0 (In Situ Cancer):
- At this stage, cancerous cells are confined to the site where they first developed and have not invaded nearby tissues or organs.
- Treatment options often involve surgical removal of the abnormal cells, with a high likelihood of complete cure.
- Stage I:
- Cancer is localized and small in size, typically limited to the tissue of origin.
- Surgical intervention, such as tumor removal, may be sufficient for treatment, with a high chance of cure.
- Stage II:
- Cancer may be larger in size or have spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes but remains confined to the primary site.
- Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy to eradicate cancerous cells and prevent further spread.
- Stage III:
- Cancer has spread more extensively to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or both, but has not yet metastasized to distant sites.
- Treatment often requires a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy to target cancer cells both locally and regionally.
- Stage IV (Metastatic Cancer):
- Cancer has metastasized to distant organs or tissues, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or brain, making treatment more challenging.
- Treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life through therapies such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or palliative care.
- Recurrent Cancer:
- In some cases, cancer may recur after initial treatment, either at the original site or in distant locations.
- Treatment options depend on factors such as the type of cancer, previous treatments received, and the individual’s overall health, with a focus on controlling disease recurrence and managing symptoms.
When to Consult a Cancer Specialist
Consulting a cancer specialist is advisable if you experience concerning symptoms, have a family history of cancer, or undergo routine screenings that detect abnormalities. Additionally, if diagnosed with cancer, seeking the expertise of an oncologist at the earliest stage enhances the chances of successful treatment and improved prognosis.
Metro Hospitals: Leaders in Cancer Care
Metro Hospitals stand at the forefront of cancer treatment, offering a multidisciplinary approach that integrates advanced technologies with compassionate care. With a team of best cancer doctors renowned for their expertise and dedication, Metro Hospitals provide personalized treatment plans tailored to meet each patient’s unique needs. From state-of-the-art diagnostic facilities to innovative treatment modalities such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy, Metro Hospitals ensure comprehensive care at every step of the cancer journey.